
- Benefits of 5S Implementation
- 5S Workplace Scan Diagnostic Checklist
- When to Use It?
What Is 5S?
5S is a workplace organization method originating from Japan that helps improve efficiency, safety, and quality. It stands for Sort, Straighten, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain—five steps designed to organize the workspace, eliminate waste, and establish disciplined routines. Widely used in lean manufacturing and continuous improvement, 5S creates a clean, structured environment that supports productivity and team ownership.
The original 5S principles come from Japan. Due to their proven value, they have been translated and restated in English. The 5S is a philosophy meant to help build a quality work environment, both physically and mentally. The 5S engages people through the use of standards and discipline. The 5S can be applied in any working area.
The elements of 5S are simple to learn and important to implement:
- Sort: Eliminate, sort out whatever is not needed.
- Straighten: Arrange the remained items which are needed so that they are ready and easy to use. Clearly identify positions for all items so that anyone can find them and return them once the task is completed.
- Shine: Clean the working area and all equipment on a regular basis in order to maintain standards and identify defects.
- Standardize: Schedule regular cleaning and maintenance, revisit the first three steps of the 5S on a recurrent basis and validate the condition of using standard procedures.
- Sustain: Make 5S and its rules a way of life.
Download our e-book
Download our free e-book to discover how GQ Interim can transform your business with expert leadership solutions!
Benefits of 5S Implementation
- Improved safety
- Higher equipment availability
- Lower defect rates and reduction in waste
- 5S becomes a fundamental business tool and key part for Kaizen
- Forms a solid foundation upon which to build continuous improvement
- Reduced costs
- Increased production agility and flexibility
- Improved employee morale, their involvement and responsibility
- Better asset utilization
- Improved performance in productivity, quality and morale leads to increased profitability
- Enhanced enterprise image to customers, suppliers, employees, and management
The picture (source: ASQ) below is an example of a 5S workplace scan diagnostic
checklist.
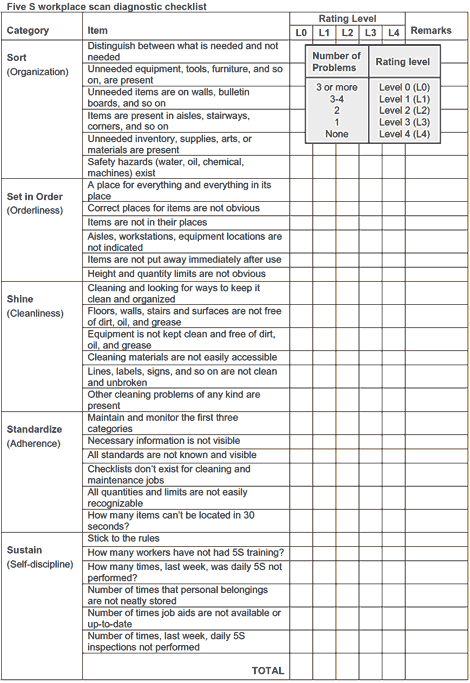
When to Use It?
5S is most effective when an organization wants to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and create a more organized and safe working environment. It should be used:
- At the start of a new project or process to establish a clean, efficient foundation
- When workspaces become cluttered, inefficient, or difficult to navigate
- As a preparation step before implementing lean or continuous improvement initiatives
- During quality or safety improvement programs to eliminate hazards and defects
- To boost employee engagement, ownership, and responsibility in maintaining standards
Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, or office settings, 5S is a powerful tool to bring structure and discipline to any work area.
Conclusion
The 5S methodology is more than just a housekeeping tool—it’s a disciplined, practical framework for creating cleaner, safer, and more efficient work environments. By focusing on organization, standardization, and sustained discipline, 5S empowers teams to reduce waste, boost productivity, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. When fully embraced, 5S becomes a foundational element of operational excellence, supporting quality, morale, and long-term profitability across any industry.
Interested in Interim Expert?
Discover how interim management can dramatically increase the efficiency of your business. Get in touch with our team to learn how working with GQ Interim will improve your company.
- Get started within few days
- Database of 10 000+ consultants
- Solving crucial problems of your business
- Custom solutions for your business needs
- Proven results with measurable impact
Related articles

- A balanced scorecard example demonstrates how organizations can measure more than just financial performance. Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, the balanced scorecard tracks goals across finance, customers, internal processes, and learning & growth. By aligning these perspectives, it ensures that daily operations support long-term strategy and sustainable growth.

- The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a structured approach to improving organizational performance by focusing on the single most limiting factor—the constraint. Whether it’s a production bottleneck, market demand, or a sales conversion gap, TOC answers three core questions—what to change, to what to change, and how to cause the change—and drives continuous improvement through five disciplined steps: identify, exploit, subordinate, elevate, and repeat.

- Software quality assurance ensures that software consistently meets stakeholder needs by preventing defects and validating that products align with defined quality attributes (e.g., reliability, security, performance). Blending defect management practices with standards-based quality models like ISO/IEC 25010 helps teams plan, measure, and continuously improve quality throughout the lifecycle.

- During our jobs we meet very often with many symbols and shortcuts or abbreviations e.g. FMEA, PPAP, CC, SC etc. When I did my first internal audit at work I had to also check the implementation of CE marking. Previously I have done the research what is this CE marking to not be absolutely lost in this area. So what is it and how is itused?