
- Background
- Methodology
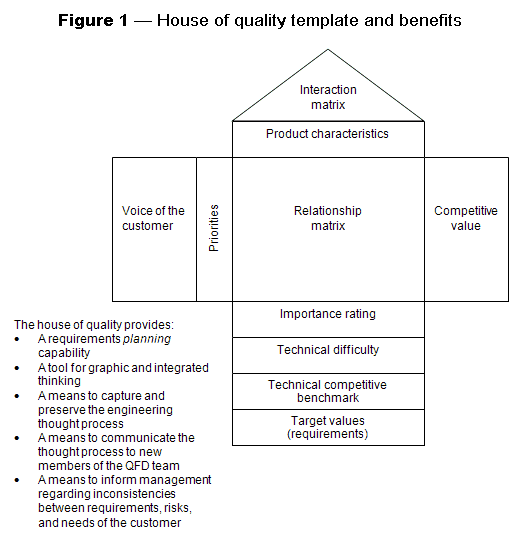
- House of Quality figure
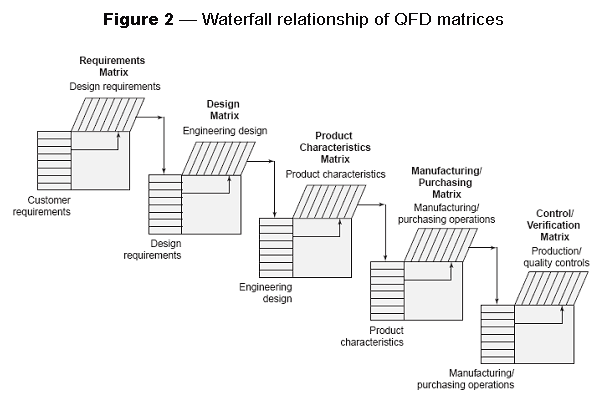
- Waterfall Relationship of QFD Matrices figure
When you are working to determine what you need to accomplish to satisfy or even delight your customers, then the tool of choice is quality function deployment or QFD.
Background
Quality professionals refer to QFD by many names, including matrix product planning, decision matrices, and customer-driven engineering. Whatever you call it, QFD is a focused methodology for carefully listening to the voice of the customer and then effectively responding to those needs and expectations. First developed in Japan in the late 1960s as a form of cause-and effect analysis, QFD was brought to the United States in the early 1980s. It gained its early popularity as a result of numerous successes in the automotive industry.
Methodology
In QFD, quality is a measure of customer satisfaction with a product or a service. QFD is a structured method that uses the seven management and planning tools to identify and prioritize customers’ expectations quickly and effectively.
Beginning with the initial matrix, commonly termed the house of quality, depicted in figure 1, the QFD methodology focuses on the most important product or service attributes or qualities. These are composed of customer wows, wants, and musts.
Once you have prioritized the attributes and qualities, QFD deploys them to the appropriate organizational function for action, as shown in figure 2. Thus, QFD is the deployment of customer driven qualities to the responsible functions of an organization.
Many QFD practitioners claim that using QFD has enabled them to reduce their product and service development cycle times by as much as 75 percent with equally impressive improvements in measured customer satisfaction.
Benefits
There are several benefits to using QFD.
Besides requiring fewer resources than other quality tools, it can:
- Improve a company’s processes, products or services.
- Produce a faster outcome than other methods can.
- Give definition to the design process.
- Help a team stay focused.
- Allow for easy management and peer review of design activities.
- Help present the information graphically.
- Leave the team well positioned in case it needs to improve upon its results for future processes, products or services.
Download our e-book
Download our free e-book to discover how GQ Interim can transform your business with expert leadership solutions!
Conclusion
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is more than a planning tool—it’s a disciplined approach that aligns business efforts with the true voice of the customer. By translating customer expectations into clearly defined priorities and actions, QFD empowers teams to streamline development, enhance satisfaction, and consistently deliver value. Whether used for internal processes or customer-facing solutions, QFD fosters focus, clarity, and measurable improvement—making it an essential methodology for any organization committed to quality-driven innovation.
Interested in Interim Expert?
Discover how interim management can dramatically increase the efficiency of your business. Get in touch with our team to learn how working with GQ Interim will improve your company.
- Get started within few days
- Database of 10 000+ consultants
- Solving crucial problems of your business
- Custom solutions for your business needs
- Proven results with measurable impact
Related articles

- A balanced scorecard example demonstrates how organizations can measure more than just financial performance. Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, the balanced scorecard tracks goals across finance, customers, internal processes, and learning & growth. By aligning these perspectives, it ensures that daily operations support long-term strategy and sustainable growth.

- The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a structured approach to improving organizational performance by focusing on the single most limiting factor—the constraint. Whether it’s a production bottleneck, market demand, or a sales conversion gap, TOC answers three core questions—what to change, to what to change, and how to cause the change—and drives continuous improvement through five disciplined steps: identify, exploit, subordinate, elevate, and repeat.

- Software quality assurance ensures that software consistently meets stakeholder needs by preventing defects and validating that products align with defined quality attributes (e.g., reliability, security, performance). Blending defect management practices with standards-based quality models like ISO/IEC 25010 helps teams plan, measure, and continuously improve quality throughout the lifecycle.

- During our jobs we meet very often with many symbols and shortcuts or abbreviations e.g. FMEA, PPAP, CC, SC etc. When I did my first internal audit at work I had to also check the implementation of CE marking. Previously I have done the research what is this CE marking to not be absolutely lost in this area. So what is it and how is itused?