
- Defect Management Approach
- Quality Attributes Approach
- ISO Software Product Quality Diagram
Software quality is a field of study and practice that describes the desirable attributes of software products.
Two approaches to software quality are prevalent:
Defect Management Approach
A software defect can be egarded as any failure to address end-user requirements. Common defects include missed or misunderstood requirements and errors in design, functional logic, data relationships, process timing, validity checking, coding, etc.
The defect management approach is based on counting and managing defects. Defects are commonly categorized by severity, and the numbers in each category are used for planning. More mature software development organizations use tools such as defect leakage matrices (for counting the numbers of defects that pass through development phases prior to detection) and control charts to measure and improve development process capability.
Quality Attributes Approach
This approach to software quality is best exemplified by fixed quality models, such as ISO/IEC 25010:2011. The quality model is the cornerstone of a product quality evaluation system. The quality model determines which quality characteristics will be taken into account when evaluating the properties of a software product.
The quality of a system is the degree to which the system satisfies the stated and implied needs of its various stakeholders, and thus provides value. Those stakeholders’ needs (functionality, performance, security, maintainability, etc.) are precisely what is represented in the quality model, which categorizes the product quality into characteristics and sub characteristics.
Download our e-book
Download our free e-book to discover how GQ Interim can transform your business with expert leadership solutions!
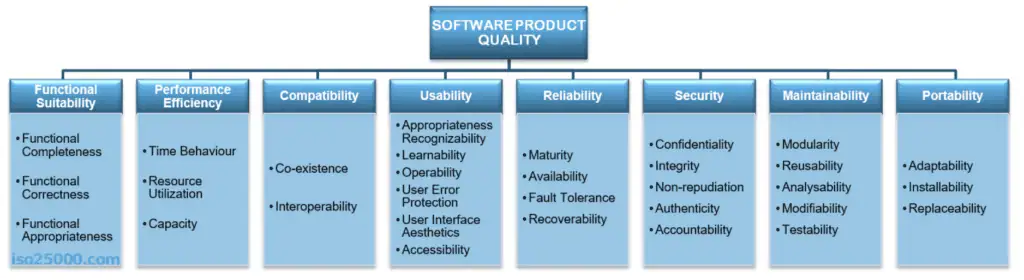
This standard describes a hierarchy of eight quality characteristics, each composed of sub-characteristics:
- Functional suitability
- Reliability
- Operability
- Performance efficiency
- Security
- Compatibility
- Maintainability
- Transferability
Additionally, the standard defines a quality in use model composed of five characteristics:
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- Satisfaction
- Safety
- Usability
Conclusion
A fixed software quality model is often helpful for considering an overall understanding of software quality. In practice, the relative importance of particular software characteristics typically depends on software domain, product type, and intended usage. Thus, software characteristics should be defined for, and used to guide the development of, each product.
Quality function deployment provides a process for developing products based on characteristics derived from user needs.
Interested in Interim Expert?
Discover how interim management can dramatically increase the efficiency of your business. Get in touch with our team to learn how working with GQ Interim will improve your company.
- Get started within few days
- Database of 10 000+ consultants
- Solving crucial problems of your business
- Custom solutions for your business needs
- Proven results with measurable impact
Related articles

- A balanced scorecard example demonstrates how organizations can measure more than just financial performance. Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, the balanced scorecard tracks goals across finance, customers, internal processes, and learning & growth. By aligning these perspectives, it ensures that daily operations support long-term strategy and sustainable growth.

- The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a structured approach to improving organizational performance by focusing on the single most limiting factor—the constraint. Whether it’s a production bottleneck, market demand, or a sales conversion gap, TOC answers three core questions—what to change, to what to change, and how to cause the change—and drives continuous improvement through five disciplined steps: identify, exploit, subordinate, elevate, and repeat.

- Software quality assurance ensures that software consistently meets stakeholder needs by preventing defects and validating that products align with defined quality attributes (e.g., reliability, security, performance). Blending defect management practices with standards-based quality models like ISO/IEC 25010 helps teams plan, measure, and continuously improve quality throughout the lifecycle.

- During our jobs we meet very often with many symbols and shortcuts or abbreviations e.g. FMEA, PPAP, CC, SC etc. When I did my first internal audit at work I had to also check the implementation of CE marking. Previously I have done the research what is this CE marking to not be absolutely lost in this area. So what is it and how is itused?